Chào ace, bài này chúng ta sẽ tìm hiểu về Đảo ngược một danh sách liên kết kép – Doubly Linked List trong series tự học về cấu trúc dữ liệu(CTDL) và giải thuật, sau đây cafedev sẽ giới thiệu và chia sẻ chi tiết(khái niệm, độ phức tạp, ứng dụng của nó, code ví dụ…) về nó thông qua các phần sau.
Trong bài học này chúng ta sẽ tìm hiểu về cách để viết một hàm có chức năng đảo ngược một Doubly Linked List cho trước.
Ví dụ, ta có một danh sách liên kết kép như sau:
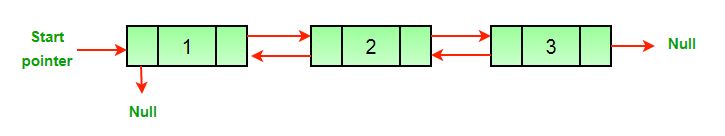
Khi tiến hành đảo ngược, danh sách liên kết kép ban đầu sẽ trở thành:
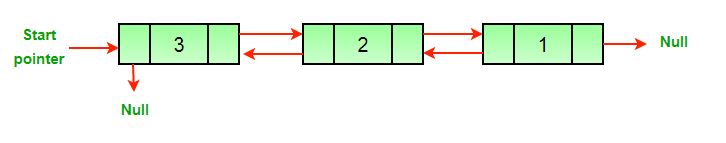
Để đảo ngược một danh sách liên kết kép, chúng ta chỉ cần:
– Hoán đổi con trỏ prev với con trỏ next, cho tất cả các nodes, thay đổi con trỏ prev của con trỏ head
– Rồi cuối cùng thay đổi con trỏ head.
Dưới đây là các đoạn code ví dụ cài đặt thuật toán đảo ngược danh sách liên kết kép được viết bằng các ngôn ngữ C++, C, Java, Python và C#:
C++
/* C++ program to reverse a doubly linked list */
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/* a node of the doubly linked list */
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
Node *prev;
};
/* Function to reverse a Doubly Linked List */
void reverse(Node **head_ref)
{
Node *temp = NULL;
Node *current = *head_ref;
/* swap next and prev for all nodes of
doubly linked list */
while (current != NULL)
{
temp = current->prev;
current->prev = current->next;
current->next = temp;
current = current->prev;
}
/* Before changing the head, check for the cases like empty
list and list with only one node */
if(temp != NULL )
*head_ref = temp->prev;
}
/* UTILITY FUNCTIONS */
/* Function to insert a node at the
beginging of the Doubly Linked List */
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
Node* new_node = new Node();
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* since we are adding at the beginning,
prev is always NULL */
new_node->prev = NULL;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* change prev of head node to new node */
if((*head_ref) != NULL)
(*head_ref)->prev = new_node ;
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list
This function is same as printList() of singly linked list */
void printList(Node *node)
{
while(node != NULL)
{
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
}
/* Driver code */
int main()
{
/* Start with the empty list */
Node* head = NULL;
/* Let us create a sorted linked list to test the functions
Created linked list will be 10->8->4->2 */
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 8);
push(&head, 10);
cout << "Original Linked list" << endl;
printList(head);
/* Reverse doubly linked list */
reverse(&head);
cout << "\nReversed Linked list" << endl;
printList(head);
return 0;
}
C
/* Program to reverse a doubly linked list */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/* a node of the doubly linked list */
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
struct Node *prev;
};
/* Function to reverse a Doubly Linked List */
void reverse(struct Node **head_ref)
{
struct Node *temp = NULL;
struct Node *current = *head_ref;
/* swap next and prev for all nodes of
doubly linked list */
while (current != NULL)
{
temp = current->prev;
current->prev = current->next;
current->next = temp;
current = current->prev;
}
/* Before changing head, check for the cases like empty
list and list with only one node */
if(temp != NULL )
*head_ref = temp->prev;
}
/* UTILITY FUNCTIONS */
/* Function to insert a node at the beginging of the Doubly Linked List */
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
struct Node* new_node =
(struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* since we are adding at the beginning,
prev is always NULL */
new_node->prev = NULL;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* change prev of head node to new node */
if((*head_ref) != NULL)
(*head_ref)->prev = new_node ;
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list
This function is same as printList() of singly linked list */
void printList(struct Node *node)
{
while(node!=NULL)
{
printf("%d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
/* Start with the empty list */
struct Node* head = NULL;
/* Let us create a sorted linked list to test the functions
Created linked list will be 10->8->4->2 */
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 8);
push(&head, 10);
printf("\n Original Linked list ");
printList(head);
/* Reverse doubly linked list */
reverse(&head);
printf("\n Reversed Linked list ");
printList(head);
getchar();
}
Java
// Java program to reverse a doubly linked list
class LinkedList {
static Node head;
static class Node {
int data;
Node next, prev;
Node(int d) {
data = d;
next = prev = null;
}
}
/* Function to reverse a Doubly Linked List */
void reverse() {
Node temp = null;
Node current = head;
/* swap next and prev for all nodes of
doubly linked list */
while (current != null) {
temp = current.prev;
current.prev = current.next;
current.next = temp;
current = current.prev;
}
/* Before changing head, check for the cases like empty
list and list with only one node */
if (temp != null) {
head = temp.prev;
}
}
/* UTILITY FUNCTIONS */
/* Function to insert a node at the beginning of the Doubly Linked List */
void push(int new_data) {
/* allocate node */
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* since we are adding at the beginning,
prev is always NULL */
new_node.prev = null;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node.next = head;
/* change prev of head node to new node */
if (head != null) {
head.prev = new_node;
}
/* move the head to point to the new node */
head = new_node;
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list
This function is same as printList() of singly linked list */
void printList(Node node) {
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
/* Let us create a sorted linked list to test the functions
Created linked list will be 10->8->4->2 */
list.push(2);
list.push(4);
list.push(8);
list.push(10);
System.out.println("Original linked list ");
list.printList(head);
list.reverse();
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("The reversed Linked List is ");
list.printList(head);
}
} Python
# Program to reverse a doubly linked list
# A node of the doubly linked list
class Node:
# Constructor to create a new node
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
self.prev = None
class DoublyLinkedList:
# Constructor for empty Doubly Linked List
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Function reverse a Doubly Linked List
def reverse(self):
temp = None
current = self.head
# Swap next and prev for all nodes of
# doubly linked list
while current is not None:
temp = current.prev
current.prev = current.next
current.next = temp
current = current.prev
# Before changing head, check for the cases like
# empty list and list with only one node
if temp is not None:
self.head = temp.prev
# Given a reference to the head of a list and an
# integer,inserts a new node on the front of list
def push(self, new_data):
# 1. Allocates node
# 2. Put the data in it
new_node = Node(new_data)
# 3. Make next of new node as head and
# previous as None (already None)
new_node.next = self.head
# 4. change prev of head node to new_node
if self.head is not None:
self.head.prev = new_node
# 5. move the head to point to the new node
self.head = new_node
def printList(self, node):
while(node is not None):
print node.data,
node = node.next
# Driver program to test the above functions
dll = DoublyLinkedList()
dll.push(2);
dll.push(4);
dll.push(8);
dll.push(10);
print "\nOriginal Linked List"
dll.printList(dll.head)
# Reverse doubly linked list
dll.reverse()
print "\n Reversed Linked List"
dll.printList(dll.head) C#
// A C# program to reverse a doubly linked list
using System;
public class LinkedList
{
static Node head;
class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next, prev;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = prev = null;
}
}
/* Function to reverse a Doubly Linked List */
void reverse()
{
Node temp = null;
Node current = head;
/* swap next and prev for all nodes of
doubly linked list */
while (current != null)
{
temp = current.prev;
current.prev = current.next;
current.next = temp;
current = current.prev;
}
/* Before changing head, check for
the cases like empty list and
list with only one node */
if (temp != null)
{
head = temp.prev;
}
}
/* UTILITY FUNCTIONS */
/* Function to insert a node at the
beginging of the Doubly Linked List */
void push(int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* since we are adding at the beginning,
prev is always NULL */
new_node.prev = null;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node.next = head;
/* change prev of head node to new node */
if (head != null)
{
head.prev = new_node;
}
/* move the head to point to the new node */
head = new_node;
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given
doubly linked list This function is
same as printList() of singly linked lsit */
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null)
{
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
/* Let us create a sorted linked list
to test the functions Created linked
list will be 10->8->4->2 */
list.push(2);
list.push(4);
list.push(8);
list.push(10);
Console.WriteLine("Original linked list ");
list.printList(head);
list.reverse();
Console.WriteLine("");
Console.WriteLine("The reversed Linked List is ");
list.printList(head);
}
} Kết quả in ra là:
Original linked list
10 8 4 2
The reversed Linked List is
2 4 8 10 Độ phức tạp về thời gian: O(n)
Chúng ta cũng có thể hoán đổi phần dữ liệu chứa trong các nodes, thay vì hoán đổi các con trỏ của các nodes để đảo ngược danh sách liên kết kép. Phương pháp đảo ngược mảng một chiều đơn giản có thể được sử dụng để hoán đổi phần dữ liệu của các nodes. Việc hoán đổi phần dữ liệu có thể trở nên tốn kém hơn (về hiệu năng) so với cách hoán đổi các con trỏ nếu kích thước của phần dữ liệu là lớn.
Nguồn và Tài liệu tiếng anh tham khảo:
Tài liệu từ cafedev:
- Full series tự học Cấu trúc dữ liệu và giải thuật từ cơ bản tới nâng cao tại đây nha.
- Ebook về Cấu trúc dữ liệu và giải thuật tại đây.
- Các series tự học lập trình khác
Nếu bạn thấy hay và hữu ích, bạn có thể tham gia các kênh sau của cafedev để nhận được nhiều hơn nữa:
Chào thân ái và quyết thắng!



![[CTDL] Tìm node có giá trị nhỏ nhất trong Binary Search Tree](https://cafedev.vn/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/cafedev-binary-tree-coloring-game-218x150.png)



![[Tự học C++] Số dấu phẩy động(float, double,…) trong C++](https://cafedev.vn/wp-content/uploads/2019/12/cafedevn_c_develoment-100x70.jpg)