Hôm nay cafedev chia sẻ cho ace một số ví dụ về việc sử dụng stack trong lập trình thực tế với các bài ví dụ hay và kinh điển. Trong phần ví dụ sẽ được code trên các ngôn ngữ khác nhau như C/C++, Java, Python….Nhằm giúp ace đang sử dụng các ngôn ngữ khác nhau hiểu nhanh và nắm vững cách dùng stack trong thực tế và khi đi làm.
Nếu ace nào chưa rõ về stack là gì?, có thể tham khảo series cấu trúc dữ liệu và giải thuật tham khảo đây..
Trong bài chúng ta sẽ áp dụng cấu trúc dữ liệu stack vào việc tìm hiểu cách duyệt một biểu thức Postfix. Nếu ace nào chưa biết về biểu thức Postfix vs infix là gì thì có thể tham khảo đây.
Ký hiệu Postfix được sử dụng để biểu diễn các biểu thức đại số. Các biểu thức được viết ở dạng hậu tố được đánh giá nhanh hơn so với ký hiệu infix vì dấu ngoặc đơn không bắt buộc trong hậu tố. Chúng ta đã thảo luận về việc chuyển đổi infix sang postfix. Trong bài đăng này, việc đánh giá các biểu thức hậu tố sẽ được thảo luận và tìm hiểu sâu hơn.
Nội dung chính
1. Sau đây là thuật toán để đánh giá các biểu thức Postfix.
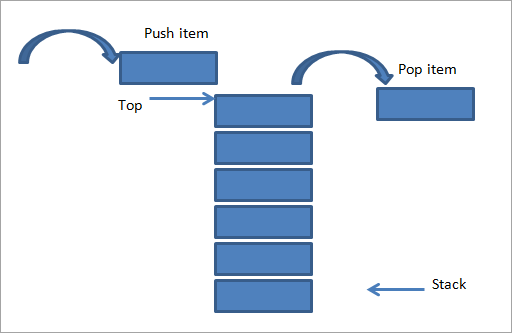
1) Tạo một stack để lưu trữ các toán hạng (hoặc giá trị).
2) Quét biểu thức đã cho và thực hiện theo các bước sau cho mọi phần tử được quét.
… ..A) Nếu phần tử là một số, hãy push nó vào stack
… ..B) Nếu phần tử là một toán tử, pop toán hạng cho toán tử từ stack. Đánh giá toán tử và push kết quả trở lại stack
3) Khi biểu thức kết thúc, số trong stack là câu trả lời cuối cùng
Chúng ta hãy tham khảo ví dụ này để hiểu hơn..
Biểu thức đã cho là “2 3 1 * + 9 -“. Chúng ta quét từng phần tử một.
1) Quét ‘2’, đó là một số, vì vậy hãy đẩy(push) nó vào ngăn xếp(stack). Ngăn xếp chứa ‘2’
2) Quét ‘3’, lại là một số, đẩy(push) nó vào ngăn xếp(stack), ngăn xếp(stack) bây giờ chứa ‘2 3’ (từ dưới lên trên)
3) Quét ‘1’, lại là một số, đẩy nó(push) vào ngăn xếp, ngăn xếp bây giờ chứa ‘2 3 1’
4) Quét ‘*’, đó là một toán tử, bật hai toán hạng từ ngăn xếp, áp dụng toán tử * trên các toán hạng, chúng ta nhận được 3 * 1 cho kết quả là 3. Chúng ta đẩy(push) kết quả ‘3’ vào ngăn xếp. Ngăn xếp bây giờ trở thành ‘2 3’.
5) Quét ‘+’, đó là một toán tử, pop hai toán hạng từ ngăn xếp, áp dụng toán tử + trên các toán hạng, chúng ta nhận được 3 + 2 cho kết quả là 5. Chúng ta đẩy kết quả ‘5’ vào ngăn xếp. Ngăn xếp bây giờ trở thành “5”.
6) Quét ‘9’, đó là một số, chúng ta đẩy nó vào ngăn xếp. Ngăn xếp bây giờ trở thành “5 9”.
7) Quét ‘-‘, đó là một toán tử, pop hai toán hạng từ ngăn xếp, áp dụng toán tử – trên các toán hạng, chúng ta nhận được 5 – 9 mà kết quả là -4. Chúng ta đẩy kết quả ‘-4’ vào ngăn xếp. Stack bây giờ trở thành ‘-4’.
8) Không còn phần tử nào để quét, chúng ta trả lại phần tử trên cùng từ ngăn xếp (là phần tử duy nhất còn lại trong ngăn xếp).
2. Dưới đây là việc thực hiện thuật toán trên
Code C++
// C++ program to evaluate value of a postfix expression
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
// Stack type
struct Stack
{
int top;
unsigned capacity;
int* array;
};
// Stack Operations
struct Stack* createStack( unsigned capacity )
{
struct Stack* stack = (struct Stack*) malloc(sizeof(struct Stack));
if (!stack) return NULL;
stack->top = -1;
stack->capacity = capacity;
stack->array = (int*) malloc(stack->capacity * sizeof(int));
if (!stack->array) return NULL;
return stack;
}
int isEmpty(struct Stack* stack)
{
return stack->top == -1 ;
}
char peek(struct Stack* stack)
{
return stack->array[stack->top];
}
char pop(struct Stack* stack)
{
if (!isEmpty(stack))
return stack->array[stack->top--] ;
return '$';
}
void push(struct Stack* stack, char op)
{
stack->array[++stack->top] = op;
}
// The main function that returns value of a given postfix expression
int evaluatePostfix(char* exp)
{
// Create a stack of capacity equal to expression size
struct Stack* stack = createStack(strlen(exp));
int i;
// See if stack was created successfully
if (!stack) return -1;
// Scan all characters one by one
for (i = 0; exp[i]; ++i)
{
// If the scanned character is an operand (number here),
// push it to the stack.
if (isdigit(exp[i]))
push(stack, exp[i] - '0');
// If the scanned character is an operator, pop two
// elements from stack apply the operator
else
{
int val1 = pop(stack);
int val2 = pop(stack);
switch (exp[i])
{
case '+': push(stack, val2 + val1); break;
case '-': push(stack, val2 - val1); break;
case '*': push(stack, val2 * val1); break;
case '/': push(stack, val2/val1); break;
}
}
}
return pop(stack);
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
char exp[] = "231*+9-";
cout<<"postfix evaluation: "<< evaluatePostfix(exp);
return 0;
}
Code C
// C program to evaluate value of a postfix expression
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Stack type
struct Stack
{
int top;
unsigned capacity;
int* array;
};
// Stack Operations
struct Stack* createStack( unsigned capacity )
{
struct Stack* stack = (struct Stack*) malloc(sizeof(struct Stack));
if (!stack) return NULL;
stack->top = -1;
stack->capacity = capacity;
stack->array = (int*) malloc(stack->capacity * sizeof(int));
if (!stack->array) return NULL;
return stack;
}
int isEmpty(struct Stack* stack)
{
return stack->top == -1 ;
}
char peek(struct Stack* stack)
{
return stack->array[stack->top];
}
char pop(struct Stack* stack)
{
if (!isEmpty(stack))
return stack->array[stack->top--] ;
return '$';
}
void push(struct Stack* stack, char op)
{
stack->array[++stack->top] = op;
}
// The main function that returns value of a given postfix expression
int evaluatePostfix(char* exp)
{
// Create a stack of capacity equal to expression size
struct Stack* stack = createStack(strlen(exp));
int i;
// See if stack was created successfully
if (!stack) return -1;
// Scan all characters one by one
for (i = 0; exp[i]; ++i)
{
// If the scanned character is an operand (number here),
// push it to the stack.
if (isdigit(exp[i]))
push(stack, exp[i] - '0');
// If the scanned character is an operator, pop two
// elements from stack apply the operator
else
{
int val1 = pop(stack);
int val2 = pop(stack);
switch (exp[i])
{
case '+': push(stack, val2 + val1); break;
case '-': push(stack, val2 - val1); break;
case '*': push(stack, val2 * val1); break;
case '/': push(stack, val2/val1); break;
}
}
}
return pop(stack);
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
char exp[] = "231*+9-";
printf ("postfix evaluation: %d", evaluatePostfix(exp));
return 0;
}
Code Java
// Java proram to evaluate value of a postfix expression
import java.util.Stack;
public class Test
{
// Method to evaluate value of a postfix expression
static int evaluatePostfix(String exp)
{
//create a stack
Stack<Integer> stack=new Stack<>();
// Scan all characters one by one
for(int i=0;i<exp.length();i++)
{
char c=exp.charAt(i);
// If the scanned character is an operand (number here),
// push it to the stack.
if(Character.isDigit(c))
stack.push(c - '0');
// If the scanned character is an operator, pop two
// elements from stack apply the operator
else
{
int val1 = stack.pop();
int val2 = stack.pop();
switch(c)
{
case '+':
stack.push(val2+val1);
break;
case '-':
stack.push(val2- val1);
break;
case '/':
stack.push(val2/val1);
break;
case '*':
stack.push(val2*val1);
break;
}
}
}
return stack.pop();
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String exp="231*+9-";
System.out.println("postfix evaluation: "+evaluatePostfix(exp));
}
} Code Python
# Python program to evaluate value of a postfix expression
# Class to convert the expression
class Evaluate:
# Constructor to initialize the class variables
def __init__(self, capacity):
self.top = -1
self.capacity = capacity
# This array is used a stack
self.array = []
# check if the stack is empty
def isEmpty(self):
return True if self.top == -1 else False
# Return the value of the top of the stack
def peek(self):
return self.array[-1]
# Pop the element from the stack
def pop(self):
if not self.isEmpty():
self.top -= 1
return self.array.pop()
else:
return "$"
# Push the element to the stack
def push(self, op):
self.top += 1
self.array.append(op)
# The main function that converts given infix expression
# to postfix expression
def evaluatePostfix(self, exp):
# Iterate over the expression for conversion
for i in exp:
# If the scanned character is an operand
# (number here) push it to the stack
if i.isdigit():
self.push(i)
# If the scanned character is an operator,
# pop two elements from stack and apply it.
else:
val1 = self.pop()
val2 = self.pop()
self.push(str(eval(val2 + i + val1)))
return int(self.pop())
# Driver program to test above function
exp = "231*+9-"
obj = Evaluate(len(exp))
print "postfix evaluation: %d"%(obj.evaluatePostfix(exp)) Code C#
// C# proram to evaluate value of a postfix expression
using System;
using System.Collections;
namespace GFG
{
class Geek
{
//Main() method
static void Main()
{
Geek e = new Geek();
e.v = ("231*+9-");
e.expression();
Console.WriteLine("postfix evaluation: " + e.answer);
Console.Read();
}
public string v;
//'v' is variable to store the string value
public string answer;
Stack i = new Stack();
//'Stack()' is inbuilt function for namespace 'System.Collections'
public void expression()
//evaluation method
{
int a, b, ans;
for (int j = 0; j < v.Length; j++)
//'v.Length' means length of the string
{
String c = v.Substring(j, 1);
if (c.Equals("*"))
{
String sa = (String)i.Pop();
String sb = (String)i.Pop();
a = Convert.ToInt32(sb);
b = Convert.ToInt32(sa);
ans = a * b;
i.Push(ans.ToString());
}
else if (c.Equals("/"))
{
String sa = (String)i.Pop();
String sb = (String)i.Pop();
a = Convert.ToInt32(sb);
b = Convert.ToInt32(sa);
ans = a / b;
i.Push(ans.ToString());
}
else if (c.Equals("+"))
{
String sa = (String)i.Pop();
String sb = (String)i.Pop();
a = Convert.ToInt32(sb);
b = Convert.ToInt32(sa);
ans = a + b;
i.Push(ans.ToString());
}
else if (c.Equals("-"))
{
String sa = (String)i.Pop();
String sb = (String)i.Pop();
a = Convert.ToInt32(sb);
b = Convert.ToInt32(sa);
ans = a - b;
i.Push(ans.ToString());
}
else
{
i.Push(v.Substring(j, 1));
}
}
answer = (String)i.Pop();
}
}
}
Kết quả:
postfix evaluation: -4Độ phức tạp thời gian của thuật toán đánh giá là O (n) với n là số ký tự trong biểu thức đầu vào.
Có những hạn chế sau của việc thực hiện ở trên.
1) Nó chỉ hỗ trợ 4 toán tử nhị phân ‘+’, ‘*’, ‘-‘ và ‘/’. Nó có thể được mở rộng cho nhiều nhà khai thác hơn bằng cách thêm nhiều trường hợp chuyển hơn.
2) Các toán hạng cho phép chỉ là các toán hạng một chữ số. Chương trình có thể được mở rộng cho nhiều chữ số bằng cách thêm một dấu phân cách giống như dấu cách giữa tất cả các phần tử (toán tử và toán hạng) của biểu thức đã cho.
3. Dưới đây là chương trình mở rộng cho phép toán hạng có nhiều chữ số.
Code C
// C program to evaluate value of a postfix
// expression having multiple digit operands
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Stack type
struct Stack
{
int top;
unsigned capacity;
int* array;
};
// Stack Operations
struct Stack* createStack( unsigned capacity )
{
struct Stack* stack = (struct Stack*) malloc(sizeof(struct Stack));
if (!stack) return NULL;
stack->top = -1;
stack->capacity = capacity;
stack->array = (int*) malloc(stack->capacity * sizeof(int));
if (!stack->array) return NULL;
return stack;
}
int isEmpty(struct Stack* stack)
{
return stack->top == -1 ;
}
int peek(struct Stack* stack)
{
return stack->array[stack->top];
}
int pop(struct Stack* stack)
{
if (!isEmpty(stack))
return stack->array[stack->top--] ;
return '$';
}
void push(struct Stack* stack,int op)
{
stack->array[++stack->top] = op;
}
// The main function that returns value
// of a given postfix expression
int evaluatePostfix(char* exp)
{
// Create a stack of capacity equal to expression size
struct Stack* stack = createStack(strlen(exp));
int i;
// See if stack was created successfully
if (!stack) return -1;
// Scan all characters one by one
for (i = 0; exp[i]; ++i)
{
//if the character is blank space then continue
if(exp[i]==' ')continue;
// If the scanned character is an
// operand (number here),extract the full number
// Push it to the stack.
else if (isdigit(exp[i]))
{
int num=0;
//extract full number
while(isdigit(exp[i]))
{
num=num*10 + (int)(exp[i]-'0');
i++;
}
i--;
//push the element in the stack
push(stack,num);
}
// If the scanned character is an operator, pop two
// elements from stack apply the operator
else
{
int val1 = pop(stack);
int val2 = pop(stack);
switch (exp[i])
{
case '+': push(stack, val2 + val1); break;
case '-': push(stack, val2 - val1); break;
case '*': push(stack, val2 * val1); break;
case '/': push(stack, val2/val1); break;
}
}
}
return pop(stack);
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
char exp[] = "100 200 + 2 / 5 * 7 +";
printf ("%d", evaluatePostfix(exp));
return 0;
} Code C++
// CPP program to evaluate value of a postfix
// expression having multiple digit operands
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Stack type
class Stack
{
public:
int top;
unsigned capacity;
int* array;
};
// Stack Operations
Stack* createStack( unsigned capacity )
{
Stack* stack = new Stack();
if (!stack) return NULL;
stack->top = -1;
stack->capacity = capacity;
stack->array = new int[(stack->capacity * sizeof(int))];
if (!stack->array) return NULL;
return stack;
}
int isEmpty(Stack* stack)
{
return stack->top == -1 ;
}
int peek(Stack* stack)
{
return stack->array[stack->top];
}
int pop(Stack* stack)
{
if (!isEmpty(stack))
return stack->array[stack->top--] ;
return '$';
}
void push(Stack* stack,int op)
{
stack->array[++stack->top] = op;
}
// The main function that returns value
// of a given postfix expression
int evaluatePostfix(char* exp)
{
// Create a stack of capacity equal to expression size
Stack* stack = createStack(strlen(exp));
int i;
// See if stack was created successfully
if (!stack) return -1;
// Scan all characters one by one
for (i = 0; exp[i]; ++i)
{
//if the character is blank space then continue
if(exp[i] == ' ')continue;
// If the scanned character is an
// operand (number here),extract the full number
// Push it to the stack.
else if (isdigit(exp[i]))
{
int num=0;
//extract full number
while(isdigit(exp[i]))
{
num = num * 10 + (int)(exp[i] - '0');
i++;
}
i--;
//push the element in the stack
push(stack,num);
}
// If the scanned character is an operator, pop two
// elements from stack apply the operator
else
{
int val1 = pop(stack);
int val2 = pop(stack);
switch (exp[i])
{
case '+': push(stack, val2 + val1); break;
case '-': push(stack, val2 - val1); break;
case '*': push(stack, val2 * val1); break;
case '/': push(stack, val2/val1); break;
}
}
}
return pop(stack);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
char exp[] = "100 200 + 2 / 5 * 7 +";
cout << evaluatePostfix(exp);
return 0;
}
Code Java
// Java proram to evaluate value of a postfix
// expression having multiple digit operands
import java.util.Stack;
class Test1
{
// Method to evaluate value of a postfix expression
static int evaluatePostfix(String exp)
{
//create a stack
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
// Scan all characters one by one
for(int i = 0; i < exp.length(); i++)
{
char c = exp.charAt(i);
if(c == ' ')
continue;
// If the scanned character is an operand
// (number here),extract the number
// Push it to the stack.
else if(Character.isDigit(c))
{
int n = 0;
//extract the characters and store it in num
while(Character.isDigit(c))
{
n = n*10 + (int)(c-'0');
i++;
c = exp.charAt(i);
}
i--;
//push the number in stack
stack.push(n);
}
// If the scanned character is an operator, pop two
// elements from stack apply the operator
else
{
int val1 = stack.pop();
int val2 = stack.pop();
switch(c)
{
case '+':
stack.push(val2+val1);
break;
case '-':
stack.push(val2- val1);
break;
case '/':
stack.push(val2/val1);
break;
case '*':
stack.push(val2*val1);
break;
}
}
}
return stack.pop();
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String exp = "100 200 + 2 / 5 * 7 +";
System.out.println(evaluatePostfix(exp));
}
} Code C#
// C# proram to evaluate value of a postfix
// expression having multiple digit operands
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
// Method to evaluate value of
// a postfix expression
public static int evaluatePostfix(string exp)
{
// create a stack
Stack<int> stack = new Stack<int>();
// Scan all characters one by one
for (int i = 0; i < exp.Length; i++)
{
char c = exp[i];
if (c == ' ')
{
continue;
}
// If the scanned character is an
// operand (number here),extract
// the number. Push it to the stack.
else if (char.IsDigit(c))
{
int n = 0;
// extract the characters and
// store it in num
while (char.IsDigit(c))
{
n = n * 10 + (int)(c - '0');
i++;
c = exp[i];
}
i--;
// push the number in stack
stack.Push(n);
}
// If the scanned character is
// an operator, pop two elements
// from stack apply the operator
else
{
int val1 = stack.Pop();
int val2 = stack.Pop();
switch (c)
{
case '+':
stack.Push(val2 + val1);
break;
case '-':
stack.Push(val2 - val1);
break;
case '/':
stack.Push(val2 / val1);
break;
case '*':
stack.Push(val2 * val1);
break;
}
}
}
return stack.Pop();
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
string exp = "100 200 + 2 / 5 * 7 +";
Console.WriteLine(evaluatePostfix(exp));
}
} Code Python
# Python program to evaluate value of a postfix
# expression with integers containing multiple digits
class evalpostfix:
def __init__(self):
self.stack =[]
self.top =-1
def pop(self):
if self.top ==-1:
return
else:
self.top-= 1
return self.stack.pop()
def push(self, i):
self.top+= 1
self.stack.append(i)
def centralfunc(self, ab):
for i in ab:
# if the component of the list is an integer
try:
self.push(int(i))
# if the component of the list is not an integer,
# it must be an operator. Using ValueError, we can
# evaluate components of the list other than type int
except ValueError:
val1 = self.pop()
val2 = self.pop()
# switch statement to perform operation
switcher ={'+':val2 + val1, '-':val2-val1, '*':val2 * val1, '/':val2 / val1, '^':val2**val1}
self.push(switcher.get(i))
return int(self.pop())
str ='100 200 + 2 / 5 * 7 +'
# splitting the given string to obtain
# integers and operators into a list
strconv = str.split(' ')
obj = evalpostfix()
print(obj.centralfunc(strconv))
Kết quả:
757Nguồn và Tài liệu tiếng anh tham khảo:
Tài liệu từ cafedev:
- Full series tự học Cấu trúc dữ liệu và giải thuật từ cơ bản tới nâng cao tại đây nha.
- Ebook về Cấu trúc dữ liệu và giải thuật tại đây.
- Các series tự học lập trình khác
Nếu bạn thấy hay và hữu ích, bạn có thể tham gia các kênh sau của cafedev để nhận được nhiều hơn nữa:
Chào thân ái và quyết thắng!



![[CTDL] Tìm node có giá trị nhỏ nhất trong Binary Search Tree](https://cafedev.vn/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/cafedev-binary-tree-coloring-game-218x150.png)



![[Tự học C++] Số dấu phẩy động(float, double,…) trong C++](https://cafedev.vn/wp-content/uploads/2019/12/cafedevn_c_develoment-100x70.jpg)