Chào ace, bài này chúng ta sẽ tìm hiểu về một trong các thuật toán sắp xếp được sử dụng nhiều trong lập trình và thực tế nhất đó là Interpolation Search, sau đây cafedev sẽ giới thiệu và chia sẻ chi tiết(khái niệm, ứng dụng của nó, code ví dụ, điểm mạnh, điểm yếu…) về Interpolation Search thông qua các phần sau.
Nội dung chính
1. Giới thiệu
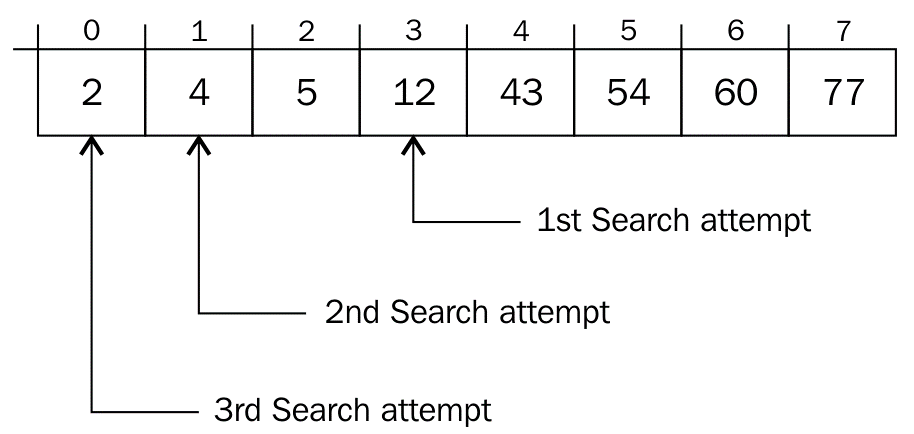
Cho một mảng được sắp xếp gồm n giá trị phân bố đều arr [], hãy viết một hàm để tìm kiếm một phần tử cụ thể x trong mảng.
Tìm kiếm tuyến tính tìm phần tử trong thời gian O (n), Tìm kiếm nhảy cần thời gian O (√ n) và Tìm kiếm nhị phân lấy thời gian O (Log n).
Tìm kiếm Nội suy(Interpolation Search) là một cải tiến so với Tìm kiếm nhị phân cho các phiên bản, trong đó các giá trị trong một mảng đã sắp xếp được phân phối đồng nhất. Tìm kiếm nhị phân luôn đi đến phần tử giữa để kiểm tra. Mặt khác, tìm kiếm nội suy(Interpolation Search) có thể đi đến các vị trí khác nhau tùy theo giá trị của khóa được tìm kiếm. Ví dụ: nếu giá trị của khóa gần với phần tử cuối cùng, thì tìm kiếm nội suy(Interpolation Search) có khả năng bắt đầu tìm kiếm về phía cuối.
Để tìm vị trí cần tìm, nó sử dụng công thức sau.
// Ý tưởng của công thức là trả về giá trị cao hơn của pos(vị trí)
// khi phần tử cần tìm gần hơn arr [hi]. Và
// giá trị nhỏ hơn khi gần arr [lo]
pos = lo + [(x-arr [lo]) * (hi-lo) / (arr [hi] -arr [Lo])]
arr [] ==> Mảng nơi các phần tử cần được tìm kiếm
Thuật toán
Phần còn lại của thuật toán Nội suy giống nhau ngoại trừ logic phân vùng ở trên.
- Bước 1: Trong một vòng lặp, hãy tính giá trị của “pos” bằng công thức vị trí đầu dò.
- Bước 2: Nếu nó trùng khớp, hãy trả về chỉ mục của mục và thoát.
- Bước 3: Nếu mục nhỏ hơn arr [pos], hãy tính toán vị trí thăm dò của mảng con bên trái. Nếu không thì tính toán tương tự trong mảng con bên phải.
- Bước 4: Lặp lại cho đến khi tìm thấy kết quả phù hợp hoặc mảng con giảm xuống 0.
2. Code ví dụ trên nhiều ngôn ngữ
2.1 Triển khai thuật toán bằng vòng lặp
C++
// C++ program to implement interpolation search
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// If x is present in arr[0..n-1], then returns
// index of it, else returns -1.
int interpolationSearch(int arr[], int n, int x)
{
// Find indexes of two corners
int lo = 0, hi = (n - 1);
// Since array is sorted, an element present
// in array must be in range defined by corner
while (lo <= hi && x >= arr[lo] && x <= arr[hi])
{
if (lo == hi)
{
if (arr[lo] == x) return lo;
return -1;
}
// Probing the position with keeping
// uniform distribution in mind.
int pos = lo + (((double)(hi - lo) /
(arr[hi] - arr[lo])) * (x - arr[lo]));
// Condition of target found
if (arr[pos] == x)
return pos;
// If x is larger, x is in upper part
if (arr[pos] < x)
lo = pos + 1;
// If x is smaller, x is in the lower part
else
hi = pos - 1;
}
return -1;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Array of items on which search will
// be conducted.
int arr[] = {10, 12, 13, 16, 18, 19, 20, 21,
22, 23, 24, 33, 35, 42, 47};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
int x = 18; // Element to be searched
int index = interpolationSearch(arr, n, x);
// If element was found
if (index != -1)
cout << "Element found at index " << index;
else
cout << "Element not found.";
return 0;
} C
// C program to implement interpolation search
#include<stdio.h>
// If x is present in arr[0..n-1], then returns
// index of it, else returns -1.
int interpolationSearch(int arr[], int n, int x)
{
// Find indexes of two corners
int lo = 0, hi = (n - 1);
// Since array is sorted, an element present
// in array must be in range defined by corner
while (lo <= hi && x >= arr[lo] && x <= arr[hi])
{
if (lo == hi){
if (arr[lo] == x) return lo;
return -1;
}
// Probing the position with keeping
// uniform distribution in mind.
int pos = lo + (((double)(hi-lo) /
(arr[hi]-arr[lo]))*(x - arr[lo]));
// Condition of target found
if (arr[pos] == x)
return pos;
// If x is larger, x is in upper part
if (arr[pos] < x)
lo = pos + 1;
// If x is smaller, x is in the lower part
else
hi = pos - 1;
}
return -1;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Array of items on which search will
// be conducted.
int arr[] = {10, 12, 13, 16, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23,
24, 33, 35, 42, 47};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
int x = 18; // Element to be searched
int index = interpolationSearch(arr, n, x);
// If element was found
if (index != -1)
printf("Element found at index %d", index);
else
printf("Element not found.");
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to implement interpolation search
class Test
{
// Array of items on which search will
// be conducted.
static int arr[] = new int[]{10, 12, 13, 16, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23,
24, 33, 35, 42, 47};
// If x is present in arr[0..n-1], then returns
// index of it, else returns -1.
static int interpolationSearch(int x)
{
// Find indexes of two corners
int lo = 0, hi = (arr.length - 1);
// Since array is sorted, an element present
// in array must be in range defined by corner
while (lo <= hi && x >= arr[lo] && x <= arr[hi])
{
if (lo == hi)
{
if (arr[lo] == x) return lo;
return -1;
}
// Probing the position with keeping
// uniform distribution in mind.
int pos = lo + (((hi-lo) /
(arr[hi]-arr[lo]))*(x - arr[lo]));
// Condition of target found
if (arr[pos] == x)
return pos;
// If x is larger, x is in upper part
if (arr[pos] < x)
lo = pos + 1;
// If x is smaller, x is in the lower part
else
hi = pos - 1;
}
return -1;
}
// Driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int x = 18; // Element to be searched
int index = interpolationSearch(x);
// If element was found
if (index != -1)
System.out.println("Element found at index " + index);
else
System.out.println("Element not found.");
}
}
Python
# Python program to implement interpolation search
# If x is present in arr[0..n-1], then returns
# index of it, else returns -1
def interpolationSearch(arr, n, x):
# Find indexs of two corners
lo = 0
hi = (n - 1)
# Since array is sorted, an element present
# in array must be in range defined by corner
while lo <= hi and x >= arr[lo] and x <= arr[hi]:
if lo == hi:
if arr[lo] == x:
return lo;
return -1;
# Probing the position with keeping
# uniform distribution in mind.
pos = lo + int(((float(hi - lo) /
( arr[hi] - arr[lo])) * ( x - arr[lo])))
# Condition of target found
if arr[pos] == x:
return pos
# If x is larger, x is in upper part
if arr[pos] < x:
lo = pos + 1;
# If x is smaller, x is in lower part
else:
hi = pos - 1;
return -1
# Driver Code
# Array of items oin which search will be conducted
arr = [10, 12, 13, 16, 18, 19, 20, 21, \
22, 23, 24, 33, 35, 42, 47]
n = len(arr)
x = 18 # Element to be searched
index = interpolationSearch(arr, n, x)
if index != -1:
print "Element found at index",index
else:
print "Element not found"
C#
// C# program to implement
// interpolation search
using System;
class GFG
{
// Array of items on which
// search will be conducted.
static int []arr = new int[]{10, 12, 13, 16, 18,
19, 20, 21, 22, 23,
24, 33, 35, 42, 47};
// If x is present in
// arr[0..n-1], then
// returns index of it,
// else returns -1.
static int interpolationSearch(int x)
{
// Find indexes of
// two corners
int lo = 0, hi = (arr.Length - 1);
// Since array is sorted,
// an element present in
// array must be in range
// defined by corner
while (lo <= hi &&
x >= arr[lo] &&
x <= arr[hi])
{
if (lo == hi)
{
if (arr[lo] == x) return lo;
return -1;
}
// Probing the position
// with keeping uniform
// distribution in mind.
int pos = lo + (((hi - lo) /
(arr[hi] - arr[lo])) *
(x - arr[lo]));
// Condition of
// target found
if (arr[pos] == x)
return pos;
// If x is larger, x
// is in upper part
if (arr[pos] < x)
lo = pos + 1;
// If x is smaller, x
// is in the lower part
else
hi = pos - 1;
}
return -1;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
int x = 18; // Element to be searched
int index = interpolationSearch(x);
// If element was found
if (index != -1)
Console.WriteLine("Element found " +
"at index " +
index);
else
Console.WriteLine("Element not found.");
}
} PHP
<?php
// PHP program to implement interpolation search
// If x is present in arr[0..n-1], then returns
// index of it, else returns -1.
function interpolationSearch($arr, $x, $n)
{
// Find indexes of two corners
$l = 0; $h = $n - 1;
// Since array is sorted, an element present
// in array must be in range defined by corner
while ($l <= $h and $x >= $arr[$l] and
$x <= $arr[$h])
{
if ($l == $h)
{
if ($arr[$l] == $x) return $l;
return -1;
}
// Probing the position with keeping
// uniform distribution in mind.
$m = intval($l + (($x - $arr[$l]) * ($h - $l) /
($arr[$h] - $arr[$l])));
// Condition of target found
if ($arr[$m] == $x)
{
return $m;
}
// If x is larger, x is in upper part
elseif ($arr[$m] < $x)
{
$l = $m + 1;
}
// If x is smaller, x is in the lower part
else
{
$h = $m - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
// Driver Code
// Array of items on which search
// will be conducted.
$arr = array(10, 12, 13, 16, 18, 19, 20, 21,
22, 23, 24, 33, 35, 42, 47);
$n = count($arr);
$x = 18; // Element to be searched
$index = interpolationSearch($arr, $x, $n);
// If element was found
if ($index != -1)
echo "Element found at index " . $index;
else
echo "Element not found.";
?>
Kết quả:
Element found at index 42.1 Triển khai thuật toán bằng đệ quy
C++
// C++ program to implement interpolation
// search with recursion
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// If x is present in arr[0..n-1], then returns
// index of it, else returns -1.
int interpolationSearch(int arr[], int lo,
int hi, int x)
{
int pos;
// Since array is sorted, an element present
// in array must be in range defined by corner
if ( lo <= hi && x >= arr[lo] &&
x <= arr[hi])
{
// Probing the position with keeping
// uniform distribution in mind.
pos = lo + (((double)( hi - lo ) /
(arr[hi] - arr[lo])) *
(x - arr[lo]));
// Condition of target found
if( arr[pos] == x )
return pos;
// If x is larger, x is in right sub array
if( arr[pos] < x )
return interpolationSearch(arr, pos + 1,
hi, x);
// If x is smaller, x is in left sub array
if( arr[pos] > x )
return interpolationSearch(arr, lo,
pos - 1, x);
}
return -1;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Array of items on which search will
// be conducted.
int arr[] = { 10, 12, 13, 16, 18,
19, 20, 21, 22, 23,
24, 33, 35, 42, 47 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Element to be searched
int x = 18;
int index = interpolationSearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x);
// If element was found
if (index != -1)
cout << "Element found at index "
<< index;
else
cout << "Element not found.";
return 0;
} C
// C program to implement interpolation search
// with recursion
#include <stdio.h>
// If x is present in arr[0..n-1], then returns
// index of it, else returns -1.
int interpolationSearch(int arr[], int lo, int hi, int x)
{
int pos;
// Since array is sorted, an element present
// in array must be in range defined by corner
if( lo <= hi && x >= arr[lo] && x <= arr[hi])
{
// Probing the position with keeping
// uniform distribution in mind.
pos = lo + ( ( (double)( hi - lo ) /
( arr[hi] - arr[lo] ) ) * ( x - arr[lo] ) );
// Condition of target found
if( arr[pos] == x )
return pos;
// If x is larger, x is in right sub array
if( arr[pos] < x )
return interpolationSearch( arr, pos+1, hi, x);
// If x is smaller, x is in left sub array
if( arr[pos] > x )
return interpolationSearch( arr, lo, pos-1, x);
}
return -1;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Array of items on which search will
// be conducted.
int arr[] = {10, 12, 13, 16, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23,
24, 33, 35, 42, 47};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
int x = 18; // Element to be searched
int index = interpolationSearch(arr, 0, n-1, x);
// If element was found
if (index != -1)
printf("Element found at index %d", index);
else
printf("Element not found.");
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to implement interpolation
// search with recursion
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// If x is present in arr[0..n-1], then returns
// index of it, else returns -1.
public static int interpolationSearch(int arr[],
int lo, int hi,
int x)
{
int pos;
// Since array is sorted, an element
// present in array must be in range
// defined by corner
if ( lo <= hi && x >= arr[lo] &&
x <= arr[hi])
{
// Probing the position with keeping
// uniform distribution in mind.
pos = lo + (((hi - lo) /
(arr[hi] - arr[lo])) *
(x - arr[lo]));
// Condition of target found
if( arr[pos] == x )
return pos;
// If x is larger, x is in right sub array
if(arr[pos] < x)
return interpolationSearch(arr, pos + 1,
hi, x);
// If x is smaller, x is in left sub array
if(arr[pos] > x)
return interpolationSearch(arr, lo,
pos - 1, x);
}
return -1;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Array of items on which search will
// be conducted.
int arr[] = { 10, 12, 13, 16, 18,
19, 20, 21, 22, 23,
24, 33, 35, 42, 47 };
int n = arr.length;
// Element to be searched
int x = 18;
int index = interpolationSearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x);
// If element was found
if (index != -1)
System.out.println("Element found at index " +
index);
else
System.out.println("Element not found.");
}
} Python3
# Python3 program to implement
# interpolation search
# with recursion
# If x is present in arr[0..n-1], then
# returns index of it, else returns -1.
def interpolationSearch(arr, lo, hi, x):
# Since array is sorted, an element present
# in array must be in range defined by corner
if (lo <= hi and x >= arr[lo] and x <= arr[hi]):
# Probing the position with keeping
# uniform distribution in mind.
pos = lo + ((hi - lo) // (arr[hi] - arr[lo]) *
(x - arr[lo]))
# Condition of target found
if arr[pos] == x:
return pos
# If x is larger, x is in right subarray
if arr[pos] < x:
return interpolationSearch(arr, pos + 1,
hi, x)
# If x is smaller, x is in left subarray
if arr[pos] > x:
return interpolationSearch(arr, lo,
pos - 1, x)
return -1
# Driver code
# Array of items in which
# search will be conducted
arr = [ 10, 12, 13, 16, 18, 19, 20, \
21, 22, 23, 24, 33, 35, 42, 47 ]
n = len(arr)
# Element to be searched
x = 18
index = interpolationSearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x)
if index != -1:
print("Element found at index", index)
else:
print("Element not found") C#
// C# program to implement
// interpolation search
using System;
class GFG{
// If x is present in
// arr[0..n-1], then
// returns index of it,
// else returns -1.
static int interpolationSearch(int []arr, int lo,
int hi, int x)
{
int pos;
// Since array is sorted, an element
// present in array must be in range
// defined by corner
if (lo <= hi && x >= arr[lo] &&
x <= arr[hi])
{
// Probing the position
// with keeping uniform
// distribution in mind.
pos = lo + (((hi - lo) /
(arr[hi] - arr[lo])) *
(x - arr[lo]));
// Condition of
// target found
if(arr[pos] == x)
return pos;
// If x is larger, x is in right sub array
if(arr[pos] < x)
return interpolationSearch(arr, pos + 1,
hi, x);
// If x is smaller, x is in left sub array
if(arr[pos] > x)
return interpolationSearch(arr, lo,
pos - 1, x);
}
return -1;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
// Array of items on which search will
// be conducted.
int []arr = new int[]{ 10, 12, 13, 16, 18,
19, 20, 21, 22, 23,
24, 33, 35, 42, 47 };
// Element to be searched
int x = 18;
int n = arr.Length;
int index = interpolationSearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x);
// If element was found
if (index != -1)
Console.WriteLine("Element found at index " +
index);
else
Console.WriteLine("Element not found.");
}
} Kết quả
Element found at index 43. Độ phức tạp
Độ phức tạp về thời gian: Nếu các phần tử được phân phối đồng đều thì O (log log n)). Trong trường hợp xấu nhất, nó có thể mất tới O (n).
Không gian phụ trợ: O (1)
Nguồn và Tài liệu tiếng anh tham khảo:
Tài liệu từ cafedev:
- Full series tự học Cấu trúc dữ liệu và giải thuật từ cơ bản tới nâng cao tại đây nha.
- Ebook về Cấu trúc dữ liệu và giải thuật tại đây.
- Các series tự học lập trình khác
Nếu bạn thấy hay và hữu ích, bạn có thể tham gia các kênh sau của cafedev để nhận được nhiều hơn nữa:
Chào thân ái và quyết thắng!








![[Tự học C++] Số dấu phẩy động(float, double,…) trong C++](https://cafedev.vn/wp-content/uploads/2019/12/cafedevn_c_develoment-100x70.jpg)