Trong bài này, chúng ta sẽ tìm hiểu về class TreeMap trong Java và các thao tác của nó qua các ví dụ.
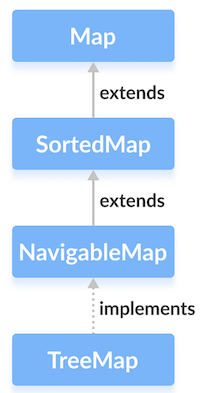
Class TreeMap của collections framework trong Java triển khai cấu trúc dữ liệu tree.
Nó triển khai NavigableMap interface.
Nội dung chính
1. Tạo TreeMap
Để tạo một TreeMap, chúng ta phải import java.util.TreeMapgói đầu tiên. Khi đã import xong, chúng ta có thể tạo TreeMap trong Java theo cách dưới đây.
TreeMap<Key, Value> numbers = new TreeMap<>();
Trong đoạn code trên, chúng ta đã tạo ra một TreeMap tên là numbers mà không có argument. Trong trường hợp này, các phần tử trong TreeMap được sắp xếp một cách tự nhiên (thứ tự tăng dần).
Tuy nhiên, chúng ta có thể tùy chỉnh việc sắp xếp các phần tử bằng cách sử dụng Comparator Interface. Chúng ta sẽ tìm hiểu về nó sau trong bài này.
Ở đây
- key – một code định danh duy nhất được sử dụng để liên kết từng phần tử (value) trong map
- value – các phần tử được liên kết bởi các key trong một map
2. Các hàm của TreeMap
Class TreeMap cung cấp hàm khác nhau cho phép chúng ta thực hiện các toán tử trên map.
3. Chèn các phần tử vào TreeMap
- put() – chèn cặp key / value được chỉ định (mục nhập) vào map
- putAll() – chèn tất cả các mục từ map được chỉ định vào map này
- putIfAbsent() – chèn cặp key / value được chỉ định vào map nếu key được chỉ định không có trong map
Ví dụ,
/*
Cafedev.vn - Kênh thông tin IT hàng đầu Việt Nam
@author cafedevn
Contact: cafedevn@gmail.com
Fanpage: https://www.facebook.com/cafedevn
Instagram: https://instagram.com/cafedevn
Twitter: https://twitter.com/CafedeVn
Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/in/cafe-dev-407054199/
*/
import java.util.TreeMap;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating TreeMap of even numbers
TreeMap<String, Integer> evenNumbers = new TreeMap<>();
// Using put()
evenNumbers.put("Two", 2);
evenNumbers.put("Four", 4);
// Using putIfAbsent()
evenNumbers.putIfAbsent("Six", 6);
System.out.println("TreeMap of even numbers: " + evenNumbers);
//Creating TreeMap of numbers
TreeMap<String, Integer> numbers = new TreeMap<>();
numbers.put("One", 1);
// Using putAll()
numbers.putAll(evenNumbers);
System.out.println("TreeMap of numbers: " + numbers);
}
}
Kết quả
TreeMap of even numbers: {Four=4, Six=6, Two=2}
TreeMap of numbers: {Four=4, One=1, Six=6, Two=2}4. Truy cập tới các phần tử của TreeMap
1. Sử dụng hàm entryset (), keyset () và value ()
- entrySet() – trả về tập hợp gồm tất cả cặp key / value (mục nhập) của treemap
- keySet() – trả về tập hợp gồm tất cả các key của TreeMap
- values() – trả về một tập hợp gồm tất cả các map của TreeMap
Ví dụ,
/*
Cafedev.vn - Kênh thông tin IT hàng đầu Việt Nam
@author cafedevn
Contact: cafedevn@gmail.com
Fanpage: https://www.facebook.com/cafedevn
Instagram: https://instagram.com/cafedevn
Twitter: https://twitter.com/CafedeVn
Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/in/cafe-dev-407054199/
*/
import java.util.TreeMap;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap<String, Integer> numbers = new TreeMap<>();
numbers.put("One", 1);
numbers.put("Two", 2);
numbers.put("Three", 3);
System.out.println("TreeMap: " + numbers);
// Using entrySet()
System.out.println("Key/Value mappings: " + numbers.entrySet());
// Using keySet()
System.out.println("Keys: " + numbers.keySet());
// Using values()
System.out.println("Values: " + numbers.values());
}
}
Kết quả
TreeMap: {One=1, Three=3, Two=2}
Key/Value mappings: [One=1, Three=3, Two=2]
Keys: [One, Three, Two]
Values: [1, 3, 2]2. Sử dụng hàm get () và getOrDefault ()
- get()- Trả về value liên kết với key được chỉ định. Trả về null nếu không tìm thấy key.
- getOrDefault()- Trả về value liên kết vớikey được chỉ định. Trả về value mặc định đã chỉ định nếu không tìm thấy key.
Ví dụ,
/*
Cafedev.vn - Kênh thông tin IT hàng đầu Việt Nam
@author cafedevn
Contact: cafedevn@gmail.com
Fanpage: https://www.facebook.com/cafedevn
Instagram: https://instagram.com/cafedevn
Twitter: https://twitter.com/CafedeVn
Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/in/cafe-dev-407054199/
*/
import java.util.TreeMap;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap<String, Integer> numbers = new TreeMap<>();
numbers.put("One", 1);
numbers.put("Two", 2);
numbers.put("Three", 3);
System.out.println("TreeMap: " + numbers);
// Using get()
int value1 = numbers.get("Three");
System.out.println("Using get(): " + value1);
// Using getOrDefault()
int value2 = numbers.getOrDefault("Five", 5);
System.out.println("Using getOrDefault(): " + value2);
}
}
Kết quả
TreeMap: {One=1, Three=3, Two=2}
Using get(): 3
Using getOrDefault(): 5Ở đây, hàm getOrDefault() không tìm thấy key five. Do đó, nó trả về value mặc định đã chỉ định 5.
5. Xóa các phần tử khỏi TreeMap
- remove(key) – trả về và xóa mục nhập được liên kết với key đã chỉ định khỏi TreeMap
- remove(key, value) – chỉ xóa mục nhập khỏi map nếu key được chỉ định liên kết với value được chỉ định và trả về giá trị boolean
Ví dụ,
import java.util.TreeMap;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap<String, Integer> numbers = new TreeMap<>();
numbers.put("One", 1);
numbers.put("Two", 2);
numbers.put("Three", 3);
System.out.println("TreeMap: " + numbers);
// remove method with single parameter
int value = numbers.remove("Two");
System.out.println("Removed value: " + value);
// remove method with two parameters
boolean result = numbers.remove("Three", 3);
System.out.println("Is the entry {Three=3} removed? " + result);
System.out.println("Updated TreeMap: " + numbers);
}
}
Kết quả
TreeMap: {One=1, Three=3, Two=2}
Removed value = 2
Is the entry {Three=3} removed? True
Updated TreeMap: {One=1}
6. Thay thế các phần tử trong TreeMap
- replace(key, value) – thay thế value liên kết với key được chỉ định với value mới
- replace(key, old, new) – chỉ thay thế value cũ bằng value mới nếu value cũ được liên kết với key đã chỉ định
- replaceAll(function) – thay thế từng value của map bằng kết quả của một chức năng đã được chỉ định
Ví dụ,
/*
Cafedev.vn - Kênh thông tin IT hàng đầu Việt Nam
@author cafedevn
Contact: cafedevn@gmail.com
Fanpage: https://www.facebook.com/cafedevn
Instagram: https://instagram.com/cafedevn
Twitter: https://twitter.com/CafedeVn
Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/in/cafe-dev-407054199/
*/
import java.util.TreeMap;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap<String, Integer> numbers = new TreeMap<>();
numbers.put("First", 1);
numbers.put("Second", 2);
numbers.put("Third", 3);
System.out.println("Original TreeMap: " + numbers);
// Using replace()
numbers.replace("Second", 22);
numbers.replace("Third", 3, 33);
System.out.println("TreeMap using replace: " + numbers);
// Using replaceAll()
numbers.replaceAll((key, oldValue) -> oldValue + 2);
System.out.println("TreeMap using replaceAll: " + numbers);
}
}
Kết quả
Original TreeMap: {First=1, Second=2, Third=3}
TreeMap using replace(): {First=1, Second=22, Third=33}
TreeMap using replaceAll(): {First=3, Second=24, Third=35}Trong chương trình trên, chú ý câu lệnh
numbers.replaceAll((key, oldValue) -> oldValue + 2);Ở đây, chúng ta đã thông qua một biểu thức lambda như là một đối số.
Hàm replaceAll() truy cập tất cả các mục của map. Sau đó, nó thay thế tất cả các phần tử bằng các value mới (được trả về từ biểu thức lambda).
7. Các hàm điều hướng
Vì class TreeMap triển khai NavigableMap, nó cung cấp các hàm khác nhau để điều hướng qua các phần tử của treemap.
7.1 Hàm First và Last
- firstKey() – trả về key đầu tiên của map
- firstEntry() – trả về cặp key / value trong key đầu tiên của map
- lastKey() – trả về key cuối cùng của map
- lastEntry() – trả về cặp key / value trong key cuối cùng của map
Ví dụ,
/*
Cafedev.vn - Kênh thông tin IT hàng đầu Việt Nam
@author cafedevn
Contact: cafedevn@gmail.com
Fanpage: https://www.facebook.com/cafedevn
Instagram: https://instagram.com/cafedevn
Twitter: https://twitter.com/CafedeVn
Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/in/cafe-dev-407054199/
*/
import java.util.TreeMap;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap<String, Integer> numbers = new TreeMap<>();
numbers.put("First", 1);
numbers.put("Second", 2);
numbers.put("Third", 3);
System.out.println("TreeMap: " + numbers);
// Using the firstKey() method
String firstKey = numbers.firstKey();
System.out.println("First Key: " + firstKey);
// Using the lastKey() method
String lastKey = numbers.lastKey();
System.out.println("Last Key: " + lastKey);
// Using firstEntry() method
System.out.println("First Entry: " + numbers.firstEntry());
// Using the lastEntry() method
System.out.println("Last Entry: " + numbers.lastEntry());
}
}Kết quả
TreeMap: {First=1, Second=2, Third=3}
First Key: First
Last Key: Third
First Entry: First=1
Last Entry: Third=37.2 Hàm Ceiling, Floor, Higher and Lower
- elevKey () – Trả về key thấp nhất trong số các key lớn hơn key đã chỉ định.
- elevEntry () – Trả về một mục được liên kết với key thấp nhất trong số tất cả các key lớn hơn key được chỉ định.
- lowKey () – Trả về key lớn nhất trong số tất cả các key nhỏ hơn key đã chỉ định.
- lowEntry () – Trả về mục được liên kết với key lớn nhất trong số tất cả các key nhỏ hơn key được chỉ định.
- ceilingKey () – Trả về key thấp nhất trong số các key lớn hơn key đã chỉ định. Nếu key được truyền dưới dạng đối số có trong map, nó sẽ trả về key đó.
- CeilingEntry () – Trả về một mục được liên kết với key thấp nhất trong số các key lớn hơn key được chỉ định. Nếu đó là một mục được liên kết với key thông qua một đối số có trong map, nó trả về mục được liên kết với key đó.
- floorKey () – Trả về key lớn nhất trong số các key nhỏ hơn key đã chỉ định. Nếu key được truyền dưới dạng đối số thì nó trả về key đó.
- floorEntry () – Trả về mục được liên kết với key lớn nhất trong số các key nhỏ hơn key được chỉ định. Nếu key được truyền dưới dạng đối số có mặt, nó sẽ trả về key đó.
Ví dụ,
/*
Cafedev.vn - Kênh thông tin IT hàng đầu Việt Nam
@author cafedevn
Contact: cafedevn@gmail.com
Fanpage: https://www.facebook.com/cafedevn
Instagram: https://instagram.com/cafedevn
Twitter: https://twitter.com/CafedeVn
Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/in/cafe-dev-407054199/
*/
import java.util.TreeMap;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap<String, Integer> numbers = new TreeMap<>();
numbers.put("First", 1);
numbers.put("Second", 5);
numbers.put("Third", 4);
numbers.put("Fourth", 6);
System.out.println("TreeMap: " + numbers);
// Using higher()
System.out.println("Using higherKey(): " + numbers.higherKey("Fourth"));
System.out.println("Using higherEntry(): " + numbers.higherEntry("Fourth"));
// Using lower()
System.out.println("\nUsing lowerKey(): " + numbers.lowerKey("Fourth"));
System.out.println("Using lowerEntry(): " + numbers.lowerEntry("Fourth"));
// Using ceiling()
System.out.println("\nUsing ceilingKey(): " + numbers.ceilingKey("Fourth"));
System.out.println("Using ceilingEntry(): " + numbers.ceilingEntry("Fourth"));
// Using floor()
System.out.println("\nUsing floorKey(): " + numbers.floorKey("Fourth"));
System.out.println("Using floorEntry(): " + numbers.floorEntry("Fourth"));
}
}Kết quả
TreeMap: {First=1, Fourth=6, Second=5, Third=4}
Using higherKey(): Second
Using higherEntry(): Second=5
Using lowerKey(): First
Using lowerEntry(): First=1
Using ceilingKey(): Fourth
Using ceilingEntry(): Fourth=6
Using floorkey(): Fourth
Using floorEntry(): Fourth=67.3 Hàm pollFirstEntry () và pollLastEntry ()
- pollFirstEntry() – trả về và xóa mục nhập được liên kết với key đầu tiên của map
- pollLastEntry() – trả về và xóa mục nhập được liên kết với key cuối cùng của map
Ví dụ,
/*
Cafedev.vn - Kênh thông tin IT hàng đầu Việt Nam
@author cafedevn
Contact: cafedevn@gmail.com
Fanpage: https://www.facebook.com/cafedevn
Instagram: https://instagram.com/cafedevn
Twitter: https://twitter.com/CafedeVn
Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/in/cafe-dev-407054199/
*/
import java.util.TreeMap;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap<String, Integer> numbers = new TreeMap<>();
numbers.put("First", 1);
numbers.put("Second", 2);
numbers.put("Third", 3);
System.out.println("TreeMap: " + numbers);
//Using the pollFirstEntry() method
System.out.println("Using pollFirstEntry(): " + numbers.pollFirstEntry());
// Using the pollLastEntry() method
System.out.println("Using pollLastEntry(): " + numbers.pollLastEntry());
System.out.println("Updated TreeMap: " + numbers);
}
}
Kết quả
TreeMap: {First=1, Second=2, Third=3}
Using pollFirstEntry(): First=1
Using pollLastEntry(): Third=3
Updated TreeMap: {Second=2}7.4 Các hàm headMap (), tailMap () và subMap ()
headMap (key, booleanValue)
Hàm headMap() trả về tất cả các cặp key / value của một treemap đứng trước key được chỉ định (được thông qua như là một đối số).
Tham số booleanValue là tùy chọn. Giá trị mặc định của nó là false.
Nếu true được thông qua như một booleanValue, hàm này cũng sẽ bao gồm cặp key / value của key được truyền dưới dạng đối số.
Ví dụ,
import java.util.TreeMap;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap<String, Integer> numbers = new TreeMap<>();
numbers.put("First", 1);
numbers.put("Second", 2);
numbers.put("Third", 3);
numbers.put("Fourth", 4);
System.out.println("TreeMap: " + numbers);
System.out.println("\nUsing headMap() Method:");
// Using headMap() with default booleanValue
System.out.println("Without boolean value: " + numbers.headMap("Fourth"));
// Using headMap() with specified booleanValue
System.out.println("With boolean value: " + numbers.headMap("Fourth", true));
}
}
Kết quả
TreeMap: {First=1, Fourth=4, Second=2, Third=3}
Using headMap() Method:
Without boolean value: {First=1}
With boolean value: {First=1, Fourth=4}
tailMap (key, booleanValue)
Hàm tailMap() trả về tất cả các cặp key / value của một treemap bắt đầu từ key được chỉ định (được thông qua như là một đối số).
booleanValue là một tham số tùy chọn. Giá trị mặc định của nó là true.
Nếu false được thông qua như một booleanValue, hàm sẽ không bao gồm cặp key / value của key được chỉ định.
Ví dụ,
/*
Cafedev.vn - Kênh thông tin IT hàng đầu Việt Nam
@author cafedevn
Contact: cafedevn@gmail.com
Fanpage: https://www.facebook.com/cafedevn
Instagram: https://instagram.com/cafedevn
Twitter: https://twitter.com/CafedeVn
Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/in/cafe-dev-407054199/
*/
import java.util.TreeMap;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap<String, Integer> numbers = new TreeMap<>();
numbers.put("First", 1);
numbers.put("Second", 2);
numbers.put("Third", 3);
numbers.put("Fourth", 4);
System.out.println("TreeMap: " + numbers);
System.out.println("\nUsing tailMap() Method:");
// Using tailMap() with default booleanValue
System.out.println("Without boolean value: " + numbers.tailMap("Second"));
// Using tailMap() with specified booleanValue
System.out.println("With boolean value: " + numbers.tailMap("Second", false));
}
}Kết quả
TreeMap: {First=1, Fourth=4, Second=2, Third=3}
Using tailMap() Method:
Without boolean value: {Second=2, Third=3}
With boolean value: {Third=3}subMap (k1, bV1, k2, bV2)
Hàm subMap() trả về tất cả các mục có liên quan với các key trong khoảng k1 và k2 bao gồm cả mục của k1.
bV1 và bV2 là các tham số boolean tùy chọn. Giá trị mặc định của bV1 là true và giá trị mặc định của bV2 là false.
Nếu false được thông qua như bv1, hàm này sẽ trả về tất cả các mục được liên kết với các key trong khoảng k1 và k2 không bao gồm mục của k1.
Nếu true được thông qua như bV2, hàm này sẽ trả về tất cả các mục được liên kết với các key trong khoảng k1 và k2 bao gồm cả mục của k2.
Ví dụ,
/*
Cafedev.vn - Kênh thông tin IT hàng đầu Việt Nam
@author cafedevn
Contact: cafedevn@gmail.com
Fanpage: https://www.facebook.com/cafedevn
Instagram: https://instagram.com/cafedevn
Twitter: https://twitter.com/CafedeVnimport java.util.TreeMap;
Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/in/cafe-dev-407054199/
*/
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap<String, Integer> numbers = new TreeMap<>();
numbers.put("First", 1);
numbers.put("Second", 2);
numbers.put("Third", 3);
numbers.put("Fourth", 4);
System.out.println("TreeMap: " + numbers);
System.out.println("\nUsing subMap() Method:");
// Using subMap() with default booleanValue
System.out.println("Without boolean value: " + numbers.subMap("Fourth", "Third"));
// Using subMap() with specified booleanValue
System.out.println("With boolean value: " + numbers.subMap("Fourth", false, "Third", true));
}
}Kết quả
TreeMap: {First=1, Fourth=2, Second=2, Third=3}
Using subMap() Method:
Without boolean value: {Fourth=4, Second=2}
With boolean value: {Second=2, Third=3}8. Các hàm khác của TreeMap
| Hàm | Mô tả |
| clone() | Tạo một bản sao của TreeMap |
| containsKey() | Tìm kiếm key được chỉ định trong TreeMap và trả về kết quả boolean |
| containsValue() | Tìm kiếm value được chỉ định trong TreeMap và trả về kết quả boolean |
| size() | Trả về kích thước của TreeMap |
| clear() | Xóa tất cả các mục khỏi TreeMap |
TreeMap Comparator
Trong tất cả các ví dụ trên, các phần tử treemap được sắp xếp một cách tự nhiên (theo thứ tự tăng dần). Tuy nhiên, chúng ta cũng có thể tùy chỉnh thứ tự các key.
Để làm điều này, chúng ta cần tạo class so sánh của riêng mình dựa trên việc key nào trong map được sắp xếp. Ví dụ,
/*
Cafedev.vn - Kênh thông tin IT hàng đầu Việt Nam
@author cafedevn
Contact: cafedevn@gmail.com
Fanpage: https://www.facebook.com/cafedevn
Instagram: https://instagram.com/cafedevn
Twitter: https://twitter.com/CafedeVn
Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/in/cafe-dev-407054199/
*/
import java.util.TreeMap;
import java.util.Comparator;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a treemap with a customized comparator
TreeMap<String, Integer> numbers = new TreeMap<>(new CustomComparator());
numbers.put("First", 1);
numbers.put("Second", 2);
numbers.put("Third", 3);
numbers.put("Fourth", 4);
System.out.println("TreeMap: " + numbers);
}
// Creating a comparator class
public static class CustomComparator implements Comparator<String> {
@Override
public int compare(String number1, String number2) {
int value = number1.compareTo(number2);
// elements are sorted in reverse order
if (value > 0) {
return -1;
}
else if (value < 0) {
return 1;
}
else {
return 0;
}
}
}
}Kết quả
TreeMap: {Third=3, Second=2, Fourth=4, First=1}Trong ví dụ trên, chúng ta đã tạo một treemap đi qua class CustomComparator như một đối số.
Class CustomComparator triển khai Comparator interface.
Sau đó chúng ta ghi đè hàm compare() để sắp xếp các phần tử theo thứ tự ngược lại.Để tìm hiểu thêm, hãy truy cập Comparator trong Java (tài liệu Java chính thức) .







![[Tự học C++] Số dấu phẩy động(float, double,…) trong C++](https://cafedev.vn/wp-content/uploads/2019/12/cafedevn_c_develoment-100x70.jpg)